Deploy DAD Project
NOTE: To run most of the command present in this tutorial we need to either be connected to our school network or use its VPN.
To deploy the project to our Kubernetes cluster we will need docker and kubectl (the Kubernetes cli).
Install kubectl
Follow these steps to install kubectl
Windows WSL | Linux
Download the binary:
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"Move binary to the sudo controller folder:
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectlsudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectlCheck:
kubectl version --clientkubectl version --clientMacOS
Download the binary:
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/darwin/amd64/kubectl" curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/darwin/amd64/kubectl"Move binary to the sudo controller folder:
chmod +x ./kubectl
sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
sudo chown root: /usr/local/bin/kubectlchmod +x ./kubectl
sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
sudo chown root: /usr/local/bin/kubectlCheck:
kubectl version --clientkubectl version --clientKubeconfig
Add the config file you got via email on to ~/.kube/config and test you connection to the cluster.
kubectl get podskubectl get podsPrepare the Deployment
This tutorial assumes that we have our project in the following folder structure:
./ -> Project Base
├── deployment -> deployment files (Dockerfiles and Kubernetes Resources)
├── laravel -> Laravel Project Root
├── vue -> Vue Project Root
|── websockets -> Node Web Sockets Project Root./ -> Project Base
├── deployment -> deployment files (Dockerfiles and Kubernetes Resources)
├── laravel -> Laravel Project Root
├── vue -> Vue Project Root
|── websockets -> Node Web Sockets Project RootTooling
The repository associated with these tutorials has all the commands defined in a justfile. Justfile is a simplified version of a Makefile and we need to install if (instructions on the github page) we want to use it. Still on this tutorial we will see all the commands so that we can run them manually if we want.
Each group has access to their own namespace on kubernetes but they need to register the images and deployments with the proper reference to the group. That reference has the format dad-group-X, where X is the group number.
Preparing Laravel
In the case of Laravel we need to make sure the database credentials and the SESSION_DOMAIN (for Sanctum) variables on the .env file are properly configured. Since we want to be able to run them locally we use the Docker file to change those variables. The only one that we must change is the group and that can be done using this flag for the docker build commmand:
-build-arg GROUP=dad-group-X-build-arg GROUP=dad-group-XPreparing Vue
In Vue's case we can take advantage of the .env files support of Vite to create a .env and a .env.production files with the following variables (again X to be replaced with the group number):
# .env
VITE_API_DOMAIN=localhost:8085
VITE_WS_CONNECTION=ws://localhost:8086
# .env.production
VITE_API_DOMAIN=api-dad-group-X.172.22.21.101.sslip.io
VITE_WS_CONNECTION=ws://ws-dad-group-X.172.22.21.101.sslip.io# .env
VITE_API_DOMAIN=localhost:8085
VITE_WS_CONNECTION=ws://localhost:8086
# .env.production
VITE_API_DOMAIN=api-dad-group-X.172.22.21.101.sslip.io
VITE_WS_CONNECTION=ws://ws-dad-group-X.172.22.21.101.sslip.ioDeploy the code
To deploy our code to the cluster we need to build or container images locally, and push them to the container registry, that in our case lives at registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io.
Present in the repository under the code folder is one called deployment. We are going to need those files.
Assuming we have a deployment folder in the same place as this tutorial repository we can run the next commands from the base of the full project. But check each command for the placement of the files and folders and change accordingly.
One important NOTE is that Kubernetes will depend on us naming the versions of our apps to re-deploy them when we change our code, so keep in mind that we need to bump the version each time we want to push a new version of our applications.
Configure Docker
Our Docker Registry does not use HTTPS so we ned to inform Docker that this registry is only available on port 80.
This is the configuration we need (this is a JSON property to be included into either existing configuration or a new JSON config by wrapping it in { }):
"insecure-registries" : [ "registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io" ]
"insecure-registries" : [ "registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io" ]On Windows and MacOS the simples way is to configure this via Docker Desktop.
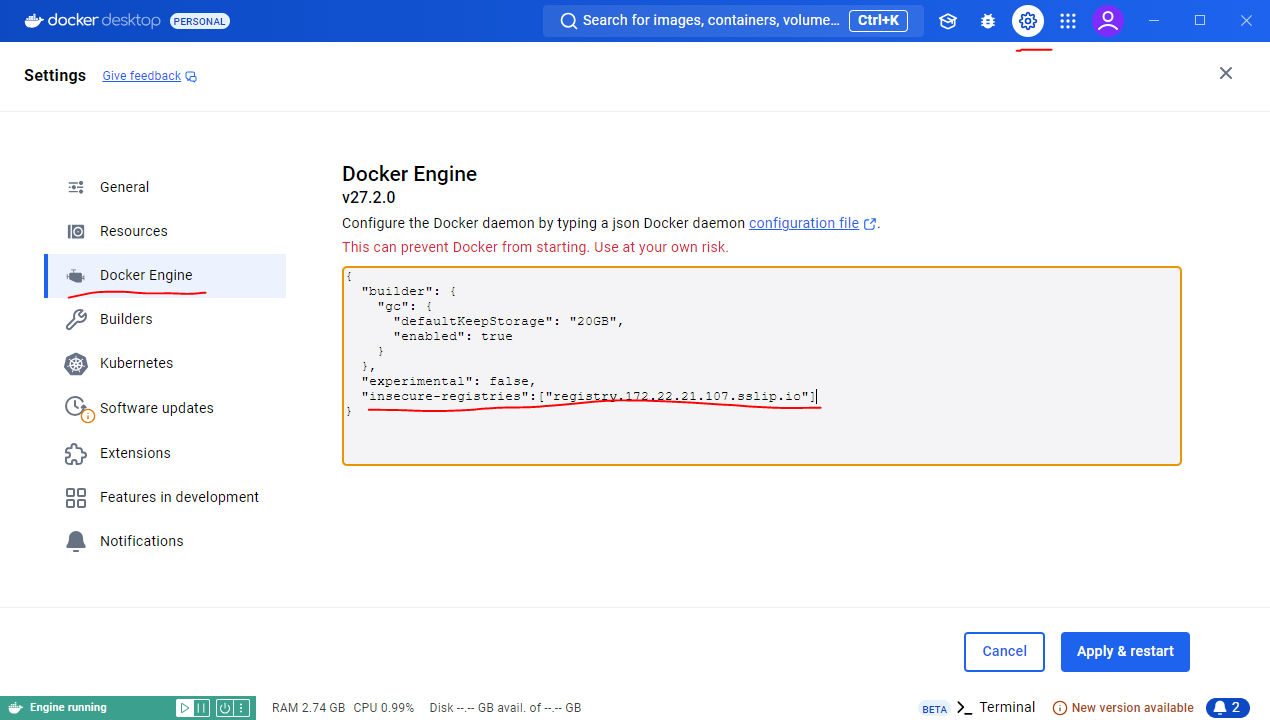
On linux we can edit the file directly via sudo nano /etc/docker/daemon.json and restart the service via sudo systemctl restart docker.
Push Images to Container Repository
Build the Laravel Image (replace group with your group id - dad-group-X and the version with the current version - 1.0.0):
docker build -t registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/api:v{{version}} \
-f ./deployment/DockerfileLaravel ./laravel \
--build-arg GROUP={{group}}docker build -t registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/api:v{{version}} \
-f ./deployment/DockerfileLaravel ./laravel \
--build-arg GROUP={{group}}Push the Laravel Image (replace group with your group id - dad-group-X and the version with the current version - 1.0.0):
docker push registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/api:v{{version}}docker push registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/api:v{{version}}Build the Vue Image (replace group with your group id - dad-group-X and the version with the current version - 1.0.0):
docker build -t registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/web:v{{version}} -f ./deployment/DockerfileVue ./vuedocker build -t registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/web:v{{version}} -f ./deployment/DockerfileVue ./vuePush the Vue Image (replace group with your group id - dad-group-X and the version with the current version - 1.0.0):
docker push registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/web:v{{version}}docker push registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/web:v{{version}}Build the Node WebSockets Image (replace group with your group id - dad-group-X and the version with the current version - 1.0.0):
docker build -t registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/ws:v{{version}} -f ./deployment/DockerfileWS ./websocketsdocker build -t registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/ws:v{{version}} -f ./deployment/DockerfileWS ./websocketsPush the Node WebSockets Image (replace group with your group id - dad-group-X and the version with the current version - 1.0.0):
docker push registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/ws:v{{version}}docker push registry.172.22.21.107.sslip.io/{{group}}/ws:v{{version}}Deploy Resources to Kubernetes Cluster
Before we can publish our Kubernetes resources we need to replace the string 'dad-groupx' in each file with our actual group (group99 is used in the code examples).
For Linux | WSL :
find ./deployment -name "*.yml" -exec sed -i "s/dad-groupx/dad-group99/g" {} +; \find ./deployment -name "*.yml" -exec sed -i "s/dad-groupx/dad-group99/g" {} +; \For MacOS:
find ./deployment -name "*.yml" -exec sed -i '' "s/dad-groupx/dad-group99/g" {} +; \find ./deployment -name "*.yml" -exec sed -i '' "s/dad-groupx/dad-group99/g" {} +; \We can now deploy our resources:
kubectl apply -f deployment/kubectl apply -f deployment/Check the deployment using:
kubectl get podskubectl get podsContainer may take a bit to get to the healthy state but after that would should be able to reach your application at:
- VUE: http://web-dad-group-x-172.22.21.101.sslip.io
- Laravel: http://api-dad-group-x-172.22.21.101.sslip.io
Running commands
We sometimes need to run commands on the containers running in the cluster, one example are the Laravel commands (like migrate), we can by using these commands (X is the group number):
# get pod name
kubectl get pods -n dad-group-X -l app=laravel-app
kubectl -n dad-group-X exec -it <pod-name> -- php artisan migrate:fresh --seed
# get pod name
kubectl get pods -n dad-group-X -l app=laravel-app
kubectl -n dad-group-X exec -it <pod-name> -- php artisan migrate:fresh --seedTo redeploy the application stack you can run:
kubectl delete -f deployment
kubectl apply -f deployment
kubectl delete -f deployment
kubectl apply -f deployment